What is Carbon Capture and Storage? Why Do We Need It?
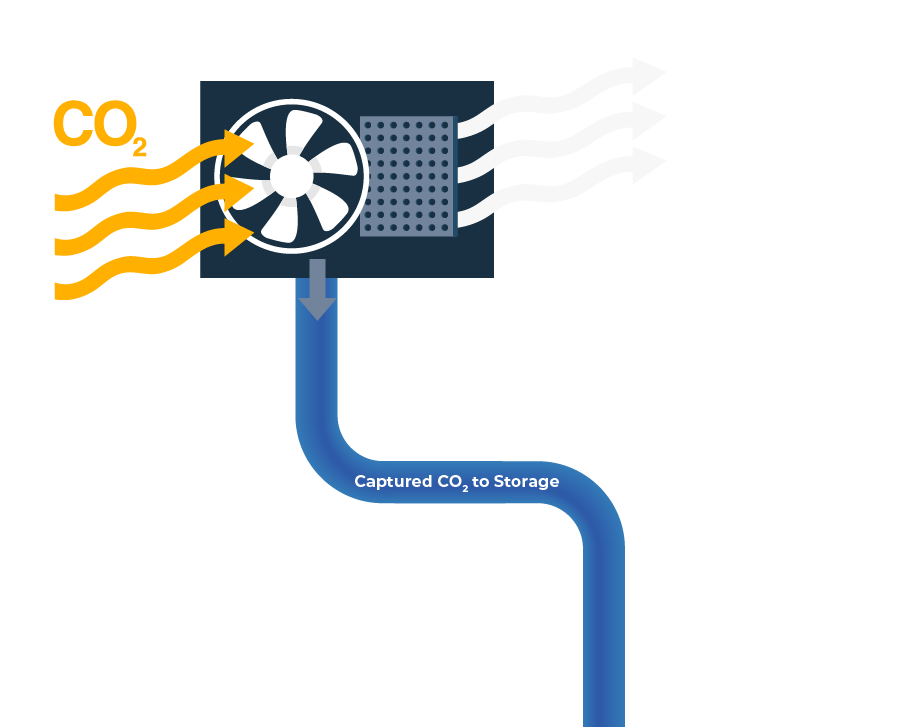
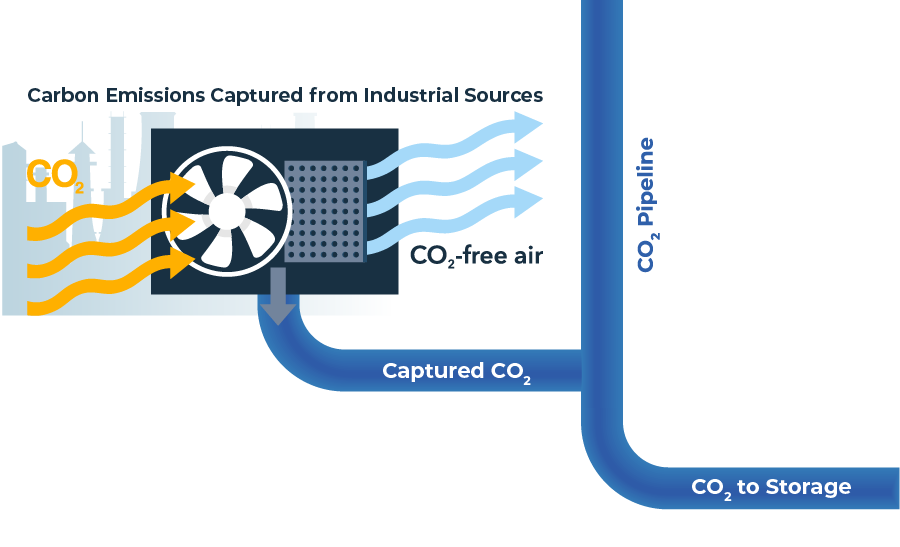
Few challenges are more important than meeting our growing demand for energy and products that support modern life, while reducing environmental impacts. In order to meet this challenge, climate experts say we will need to use a mix of sustainable strategies, including Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS). CCS is the process of capturing CO2 emissions that would have been released into the air and transporting them through CO2 pipelines to deep underground storage sites, permanently removing them from the environment.
CCS is not new; CCS projects have been operating around the world for decades. However, in order to meet our climate goals, we will need to greatly expand the effort, starting with the industries that produce the most carbon emissions. In fact, without CCS many of these industries would struggle to meet climate targets, and thus be at risk for closure.
What is Carbon Capture and Storage? Why Do We Need It?

Few challenges are more important than meeting our growing demand for energy and products that support modern life, while reducing environmental impacts. In order to meet this challenge, climate experts say we will need to use a mix of sustainable strategies, including Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS). CCS is the process of capturing CO2 emissions that would have been released into the air and transporting them through CO2 pipelines to deep underground storage sites, permanently removing them from the environment.
CCS is not new; CCS projects have been operating around the world for decades. However, in order to meet our climate goals, we will need to greatly expand the effort, starting with the industries that produce the most carbon emissions. In fact, without CCS many of these industries would struggle to meet climate targets, and thus be at risk for closure.
What is Carbon Capture and Storage? Why Do We Need It?
Few challenges are more important than meeting our growing demand for energy and products that support modern life, while reducing environmental impacts. In order to meet this challenge, climate experts say we will need to use a mix of sustainable strategies, including Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS). CCS is the process of capturing CO2 emissions that would have been released into the air and transporting them through CO2 pipelines to deep underground storage sites, permanently removing them from the environment.
CCS is not new; CCS projects have been operating around the world for decades. However, in order to meet our climate goals, we will need to greatly expand the effort, starting with the industries that produce the most carbon emissions. In fact, without CCS many of these industries would struggle to meet climate targets, and thus be at risk for closure.

CO2 Pipelines Are Needed for Carbon Capture
We can now capture carbon emissions instead of releasing them into the atmosphere. Pipelines are needed to deliver those emissions from where they’re captured to their permanent underground storage area hundreds or potentially thousands of miles away.
How Permanent Storage Works
Storing carbon dioxide (CO2) is like the reverse of drilling for natural gas. Instead of drilling through rock to let the trapped gas out, CO2 is injected thousands of feet underground by thick, impermeable rocks that act as a lid to keep the stored CO2 in place. They are similar to the rocks that have kept oil, natural gas and naturally occurring CO2 underground for millions of years.
Potential CO2 storage sites are carefully selected only after undergoing rigorous analysis to ensure they are geologically suitable. This analysis helps mitigate the risk of the CO2 migrating to other formations or to the atmosphere. The CO2 is also stored thousands of feet underground, well below any sources of drinking water, or under the sea floor.
- Industry has been safely injecting CO2 around the world for decades, successfully demonstrating the capability to safely and permanently store CO2.
- Naturally occurring underground deposits of CO2, like in nearby Mississippi, have stayed locked deep underground for millions of years.
Once stored, the storage sites are constantly monitored. A combination of technologies is used to detect any potential leads at the atmospheric, near-surface and deep sub-surface levels, including optical laser sensors, pressure-monitoring transponders and 4D seismicity technology.
CO2 Pipelines and Underground Storage Will Secure LA’s Energy Future
The energy and industrial jobs that are so important to the Louisiana economy will struggle to reduce their carbon emissions to the point that they can continue to employ the thousands of people they do today.
Capturing their carbon emissions before they are released into the air and storing them away permanently will both help the environment and help these critical industries meet climate targets, sustaining these jobs and the Louisiana economy during the energy transition.
Because Louisiana is blessed with some of the best and safest underground storage areas, the added advantage is that Louisiana can lead the energy transition and develop a new low carbon economy. According to the 2019 National Petroleum Council (NPC) CCS report, Meeting the Dual Challenge, jobs associated with CCS investment in the U.S. could grow from about 10,000 per year initially, to more than 200,000 per year by 2050.
- But here’s the challenge: The places where CO2 emissions are produced and captured are a distance away from locations along the Gulf Coast where we can store them.
The solution is building new pipelines to safely transport the carbon emissions from the sources to the storage areas, which in turn will create new jobs at the same time.
CO2 Pipelines and Underground Storage Will Secure LA’s Energy Future
The energy and industrial jobs that are so important to the Louisiana economy will struggle to reduce their carbon emissions to the point that they can continue to employ the thousands of people they do today.
Capturing their carbon emissions before they are released into the air and storing them away permanently will both help the environment and help these critical industries meet climate targets, sustaining these jobs and the Louisiana economy during the energy transition.
Because Louisiana is blessed with some of the best and safest underground storage areas, the added advantage is that Louisiana can lead the energy transition and develop a new low carbon economy. According to the 2019 National Petroleum Council (NPC) CCS report, Meeting the Dual Challenge, jobs associated with CCS investment in the U.S. could grow from about 10,000 per year initially, to more than 200,000 per year by 2050.
But here’s the challenge: The places where CO2 emissions are produced and captured are a distance away from locations along the Gulf Coast where we can store them.
The solution is building new pipelines to safely transport the carbon emissions from the sources to the storage areas, which in turn will create new jobs at the same time.
Why Louisiana?
Louisiana has a special combination of energy and industrial jobs we need to keep and the natural geology deep underground needed to safely store their carbon emissions.
Louisiana has a long, proven history of safe underground storage operations. America’s underground Strategic Petroleum Reserve is an example – two storage sites have been operating safely beneath Iberville and Cameron Parishes for more than 30 years.
- Extensive research has identified the best, safest underground CO2 storage spaces, and Louisiana has an abundance of them.
Louisiana’s heavy industrial job base would be hard to sustain without capturing and storing carbon emissions.
Benefits of New CO2 Pipelines
Federal Government Pipeline Safety Requirements
- Congress in the Pipeline Safety Reauthorization Act of 1988 required the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) to regulate CO2 pipelines.
- The U.S. Department of Pipelines and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration (PHMSA) in 1989 expanded its federal regulations for similar systems like crude oil and refined products to also cover CO2 pipelines.
- PHMSA inspects and enforces compliance with potential fines on pipeline operators violating federal CO2 pipeline safety requirements.
CO2 Pipeline Operations Safety
Current federal law and government pipeline safety regulation requires CO2 pipeline operators to proactively inspect their pipelines and conduct preventive maintenance. Pipeline personnel monitor operations 24/7 and can shut down a CO2 pipeline if there is a problem. CO2 pipelines are constructed with high-grade steel and a protective coating to help prevent corrosion.
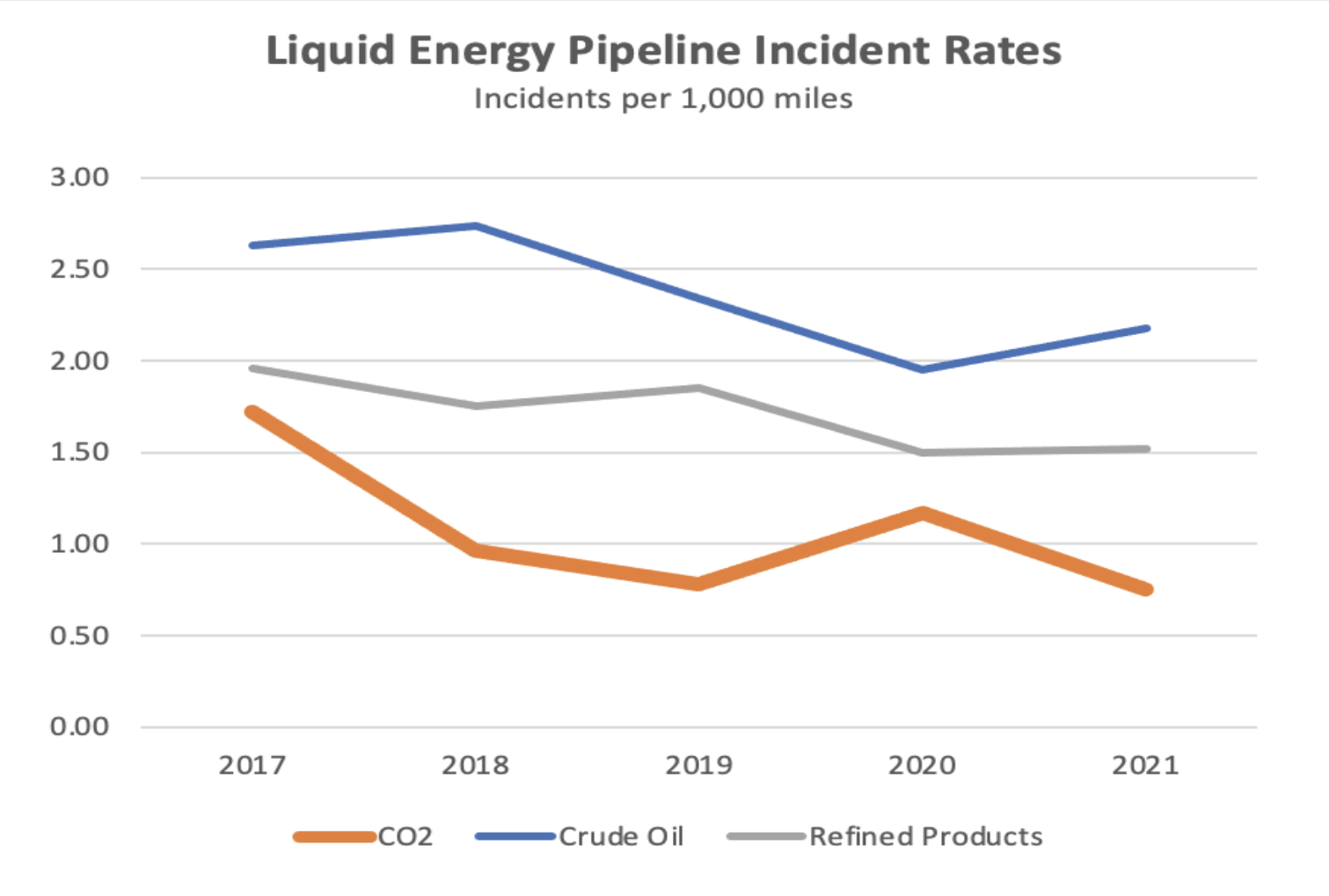
While incidents are rare and federal government safety data shows CO2 pipelines are some of the safest pipelines in operation, it’s still important to be prepared for anything. That’s why the industry is committed to providing first responders with emergency responder training programs, including CO2, to help keep our parishes safe.
Hi-Tech Inspection Tools
Preventive Maintenance
24/7 Monitoring
Hi-Grade Steel & Protective Coatings
CO2 Storage Safety in Action
Just like the U.S. DOT and PHMSA regulate pipelines, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency regulates this underground storage.
Government regulations require extensive study of the underground geology to demonstrate a site is safe for CO2 storage. Louisiana is blessed to have large areas, especially along the Gulf Coast, that meet or exceed these requirements.
Underground storage sites must meet federal construction, operations, monitoring and recordkeeping requirements.
Why Do We Need More CO2 Pipelines?
Information on how pipelines work, how they are constructed and what pipeline operators do to keep them safe.
Pipelines deliver the benefits of affordable energy, helping us get where we need to go and making life more convenient.
Proactive inspections, preventive maintenance, and 24/7 monitoring all keep pipelines and surrounding areas safe.